什么是单点登录?
我想肯定有一部分人“望文生义”的认为单点登录就是一个用户只能在一处登录,其实这是错误的理解(我记得我第一次也是这么理解的)。
单点登录指的是多个子系统只需要登录一个,其他系统不需要登录了(一个浏览器内)。一个子系统退出,其他子系统也全部是退出状态。
如果你还是不明白,我们举个实际的例子把。比如博客园首页:https://www.cnblogs.com,和博客园的找找看http://zzk.cnblogs.com。这就是两个系统(不同的域名)。如果你登录其中一个,另一个也是登录状态。如果你退出一个,另一个也是退出状态了。.那么这是怎么实现的呢?这就是我们今天要分析的问题了。
单点登录(SSO)原理
-
首先我们需要一个认证中心(Service),和两个子系统(Client)。
-
当浏览器第一次访问Client1时,处于未登录状态 -> 302到认证中心(Service) -> 在Service的登录页面登录(写入Cookie记录登录信息) -> 302到Client1(写入Cookie记录登录信息)
-
第二次访问Client1 -> 读取Client1中Cookie登录信息 -> Client1为登录状态
-
第一次访问Client2 -> 读取Client2中Cookie中的登录信息 -> Client2为未登录状态 -> 302到在Service(读取Service中的Cookie为登录状态) -> 302到Client2(写入Cookie记录登录信息)
我们发现在访问Client2的时候,中间时间经过了几次302重定向,并没有输入用户名密码去登录。用户完全感觉不到,直接就是登录状态了。
图解: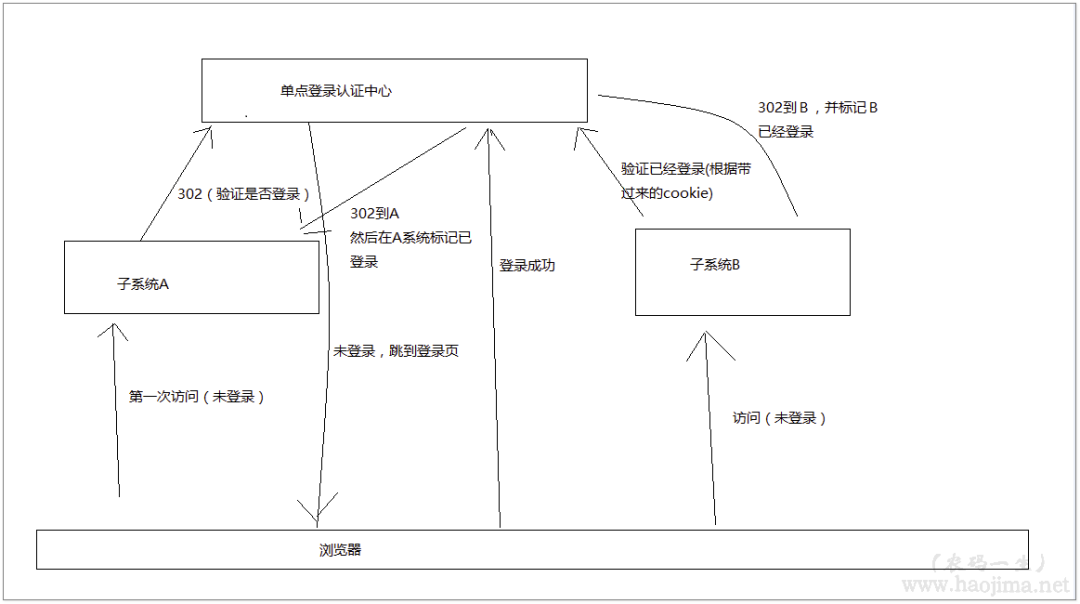
手撸一个SSO
环境:.NET Framework 4.5.2
Service:
/// <summary>/// 登录/// </summary>/// <param name="name"></param>/// <param name="passWord"></param>/// <param name="backUrl"></param>/// <returns></returns>[HttpPost]public string Login(string name, string passWord, string backUrl){if (true)//TODO:验证用户名密码登录{//用Session标识会话是登录状态Session["user"] = "XX已经登录";//在认证中心 保存客户端Client的登录认证码TokenIds.Add(Session.SessionID, Guid.NewGuid());}else//验证失败重新登录{return "/Home/Login";}return backUrl + "?tokenId=" + TokenIds[Session.SessionID];//生成一个tokenId 发放到客户端}
Client:
public static List<string> Tokens = new List<string>();public async Task<ActionResult> Index(){var tokenId = Request.QueryString["tokenId"];//如果tokenId不为空,则是由Service302过来的。if (tokenId != null){using (HttpClient http = new HttpClient()){//验证Tokend是否有效var isValid = await http.GetStringAsync("http://localhost:8018/Home/TokenIdIsValid?tokenId=" + tokenId);if (bool.Parse(isValid.ToString())){if (!Tokens.Contains(tokenId)){//记录登录过的Client (主要是为了可以统一登出)Tokens.Add(tokenId);}Session["token"] = tokenId;}}}//判断是否是登录状态if (Session["token"] == null || !Tokens.Contains(Session["token"].ToString())){return Redirect("http://localhost:8018/Home/Verification?backUrl=http://localhost:26756/Home");}else{if (Session["token"] != null)Session["token"] = null;}return View();}
效果图: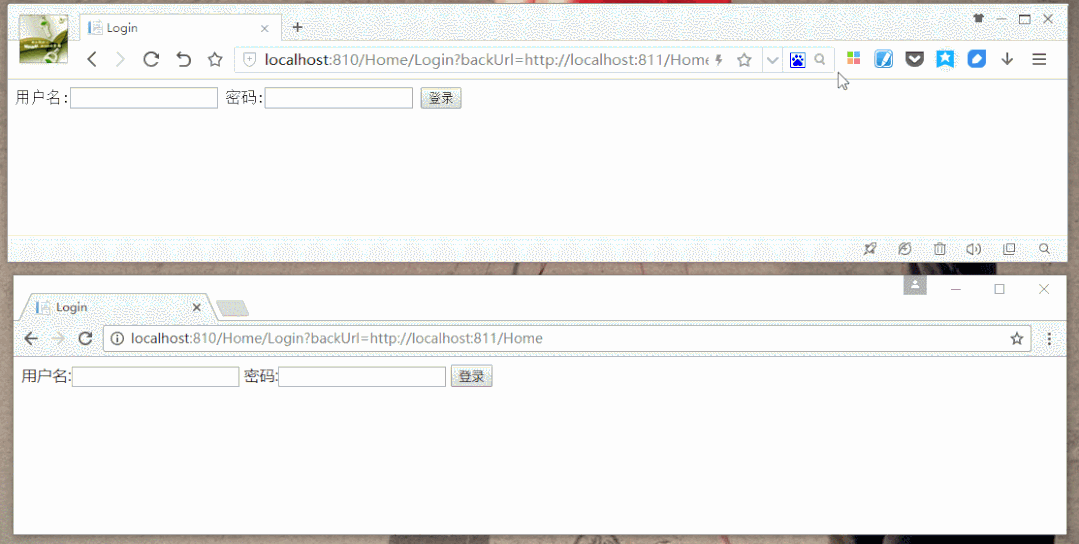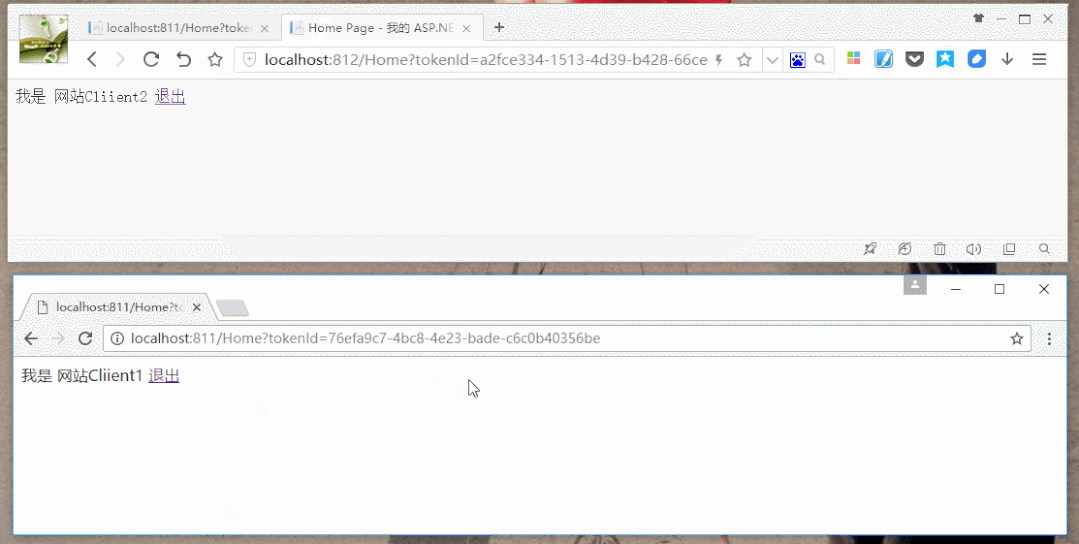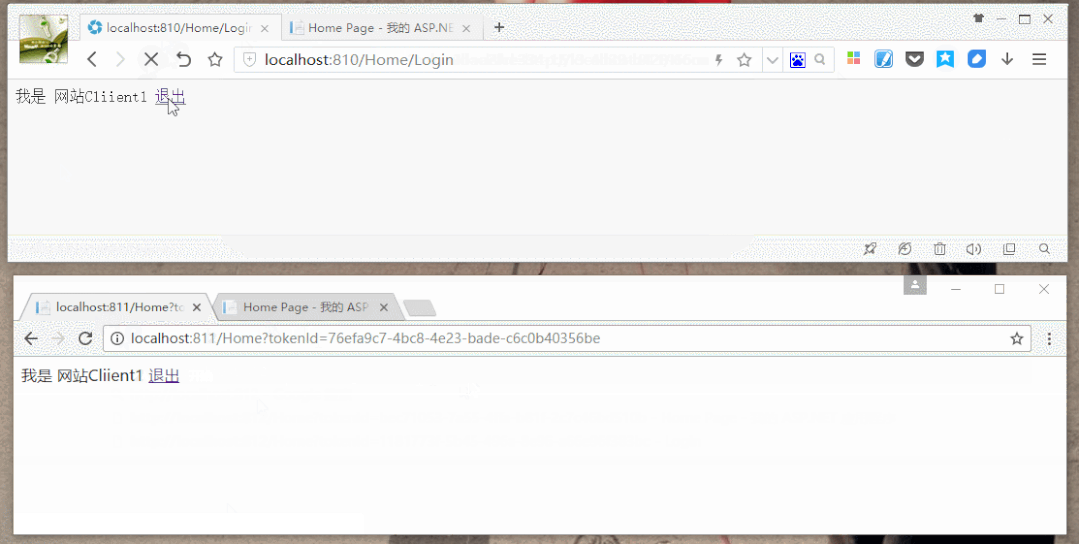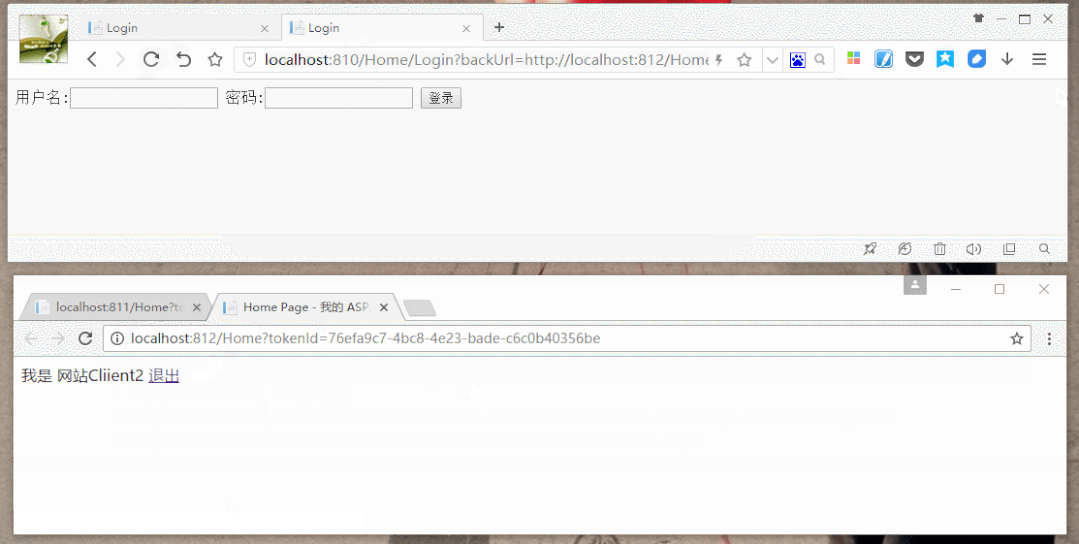
当然,这只是用较少的代码撸了一个较简单的SSO。仅用来理解,勿用于实际应用。
IdentityServer4实现SSO
环境:.NET Core 2.0
上面我们手撸了一个SSO,接下来我们看看.NET里的IdentityServer4怎么来使用SSO。
首先建一个IdentityServer4_SSO_Service(MVC项目),再建两个IdentityServer4_SSO_Client(MVC项目)
在Service项目中用nuget导入IdentityServer4 2.0.2、IdentityServer4.AspNetIdentity 2.0.0、IdentityServer4.EntityFramework 2.0.0
在Client项目中用nuget导入IdentityModel 2.14.0
然后分别设置Service和Client项目启动端口为 5001(Service)、5002(Client1)、5003(Client2)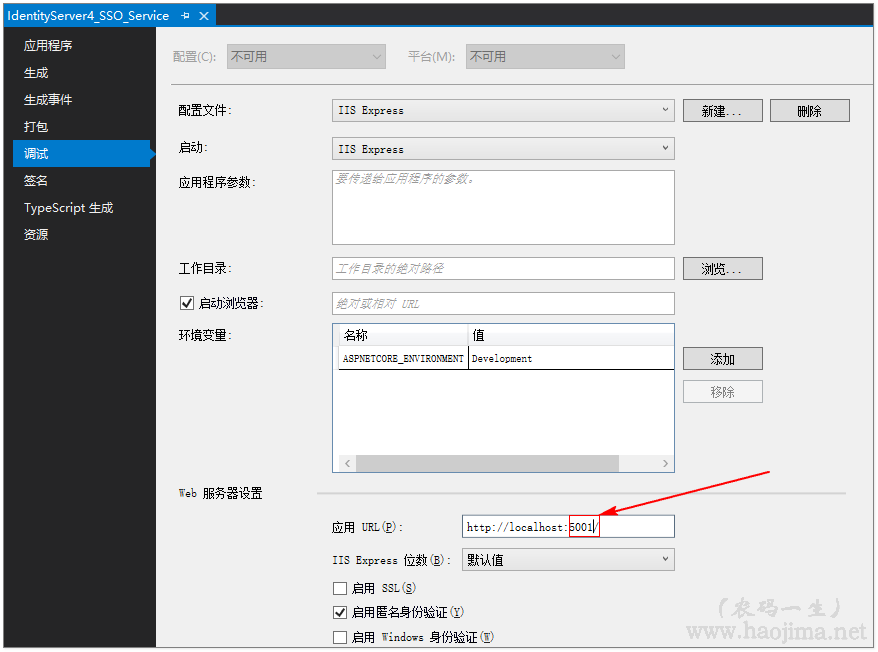
在Service中新建一个类Config:
public class Config{public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources(){return new List<IdentityResource>{new IdentityResources.OpenId(),new IdentityResources.Profile(),};}public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources(){return new List<ApiResource>{new ApiResource("api1", "My API")};}// 可以访问的客户端public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients(){return new List<Client>{// OpenID Connect hybrid flow and client credentials client (MVC)//Client1new Client{ClientId = "mvc1",ClientName = "MVC Client1",AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.HybridAndClientCredentials,RequireConsent = true,ClientSecrets ={new Secret("secret".Sha256())},RedirectUris = { "http://localhost:5002/signin-oidc" }, //注意端口5002 是我们修改的Client的端口PostLogoutRedirectUris = { "http://localhost:5002/signout-callback-oidc" },AllowedScopes ={IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,"api1"},AllowOfflineAccess = true},//Client2new Client{ClientId = "mvc2",ClientName = "MVC Client2",AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.HybridAndClientCredentials,RequireConsent = true,ClientSecrets ={new Secret("secret".Sha256())},RedirectUris = { "http://localhost:5003/signin-oidc" },PostLogoutRedirectUris = { "http://localhost:5003/signout-callback-oidc" },AllowedScopes ={IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId,IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile,"api1"},AllowOfflineAccess = true}};}}
新增一个ApplicationDbContext类继承于IdentityDbContext:
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<IdentityUser>{public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options): base(options){}protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder){base.OnModelCreating(builder);}}
在文件appsettings.json中配置数据库连接字符串:
"ConnectionStrings": {"DefaultConnection": "Server=(local);Database=IdentityServer4_Demo;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"}
在文件Startup.cs的ConfigureServices方法中增加:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))); //数据库连接字符串services.AddIdentity<IdentityUser, IdentityRole>().AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>().AddDefaultTokenProviders();services.AddMvc();string connectionString = Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection");var migrationsAssembly = typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.GetName().Name;services.AddIdentityServer().AddDeveloperSigningCredential().AddAspNetIdentity<IdentityUser>().AddConfigurationStore(options =>{options.ConfigureDbContext = builder =>builder.UseSqlServer(connectionString,sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(migrationsAssembly));}).AddOperationalStore(options =>{options.ConfigureDbContext = builder =>builder.UseSqlServer(connectionString,sql => sql.MigrationsAssembly(migrationsAssembly));options.EnableTokenCleanup = true;options.TokenCleanupInterval = 30;});}
并在Startup.cs文件里新增一个方法InitializeDatabase(初始化数据库):
/// <summary>/// 初始数据库/// </summary>/// <param name="app"></param>private void InitializeDatabase(IApplicationBuilder app){using (var serviceScope = app.ApplicationServices.GetService<IServiceScopeFactory>().CreateScope()){serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ApplicationDbContext>().Database.Migrate();//执行数据库迁移serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<PersistedGrantDbContext>().Database.Migrate();var context = serviceScope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<ConfigurationDbContext>();context.Database.Migrate();if (!context.Clients.Any()){foreach (var client in Config.GetClients())//循环添加 我们直接添加的 5002、5003 客户端{context.Clients.Add(client.ToEntity());}context.SaveChanges();}if (!context.IdentityResources.Any()){foreach (var resource in Config.GetIdentityResources()){context.IdentityResources.Add(resource.ToEntity());}context.SaveChanges();}if (!context.ApiResources.Any()){foreach (var resource in Config.GetApiResources()){context.ApiResources.Add(resource.ToEntity());}context.SaveChanges();}}}
修改Configure方法:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env){//初始化数据InitializeDatabase(app);if (env.IsDevelopment()){app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();app.UseBrowserLink();app.UseDatabaseErrorPage();}else{app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");}app.UseStaticFiles();app.UseIdentityServer();app.UseMvc(routes =>{routes.MapRoute(name: "default",template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");});}
然后新建一个AccountController控制器,分别实现注册、登录、登出等。
新建一个ConsentController控制器用于Client回调。
然后在Client的Startup.cs类里修改ConfigureServices方法:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){services.AddMvc();JwtSecurityTokenHandler.DefaultInboundClaimTypeMap.Clear();services.AddAuthentication(options =>{options.DefaultScheme = "Cookies";options.DefaultChallengeScheme = "oidc";}).AddCookie("Cookies").AddOpenIdConnect("oidc", options =>{options.SignInScheme = "Cookies";options.Authority = "http://localhost:5001";options.RequireHttpsMetadata = false;options.ClientId = "mvc2";options.ClientSecret = "secret";options.ResponseType = "code id_token";options.SaveTokens = true;options.GetClaimsFromUserInfoEndpoint = true;options.Scope.Add("api1");options.Scope.Add("offline_access");});}对于Client的身份认证就简单了:
[Authorize]//身份认证public IActionResult Index(){return View();}/// <summary>/// 登出/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public async Task<IActionResult> Logout(){await HttpContext.SignOutAsync("Cookies");await HttpContext.SignOutAsync("oidc");return View("Index");}
效果图: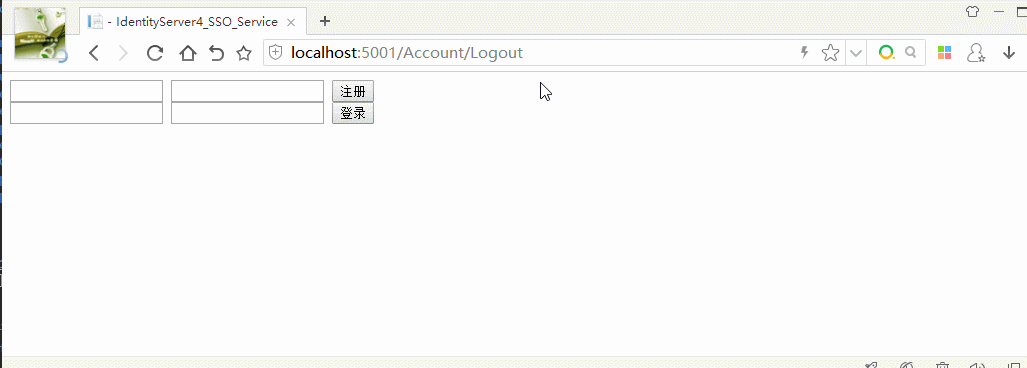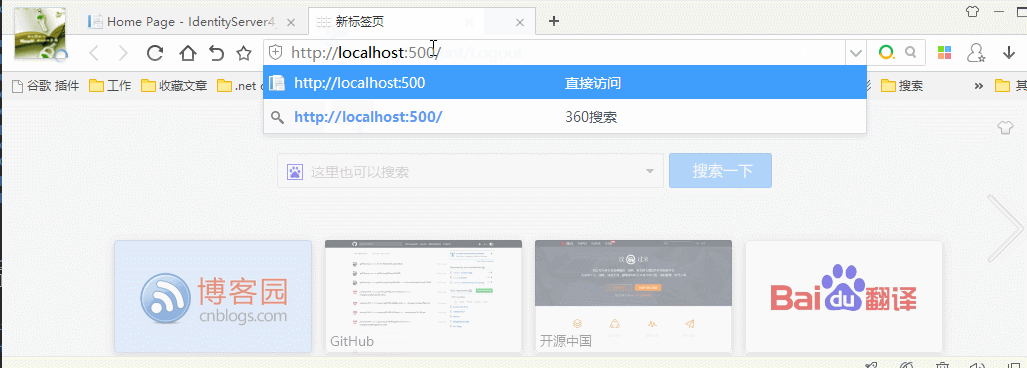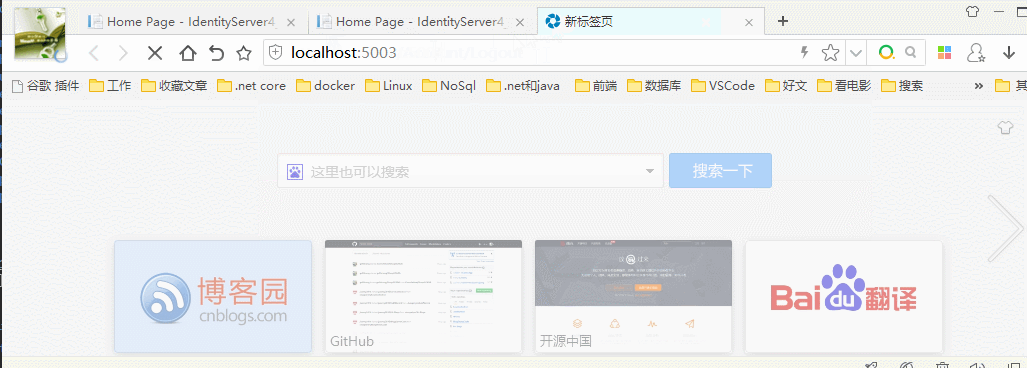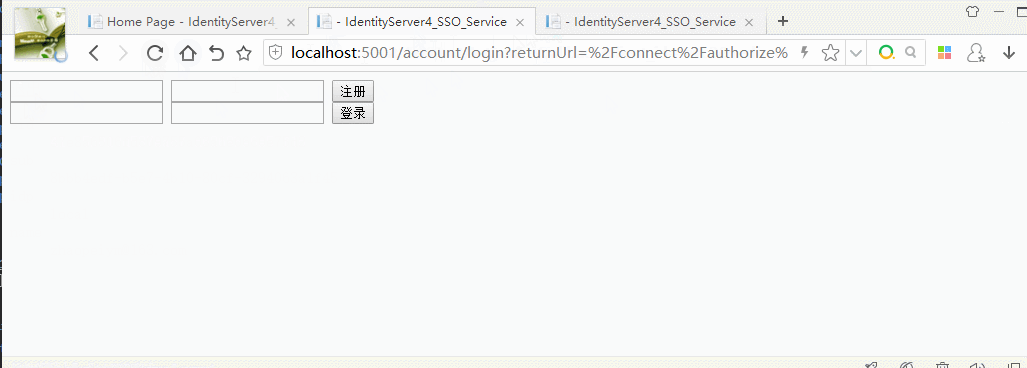
源码地址(demo可配置数据库连接后直接运行)
-
https://github.com/zhaopeiym/BlogDemoCode/tree/master/sso(单点登录)
