学习好c#就要了解C#底层原理,今天聊聊IEnumerable、IEnumerator和foreach的联系与解析,基础没有掌握好的理解有点费劲。
1、关于foreach和for
foreach和for都是循环的关键字,使用这两个关键字可以对集合对象进行遍历,获取里面每一个对象的信息进行操作。.
static void Main(string[] args){ string[] strList = new string[]{ "1","2","3","4"}; for (int i = 0; i < strList.Length; i++){Console.WriteLine(strList[i]);} foreach (string str in strList){Console.WriteLine(str);}Console.ReadKey();}
上面结果的输出都是一样的,我们来看看IL是否是一样的。
IL_002c: br.s IL_003d //for开始的地方IL_002e: nopIL_002f: ldloc.0IL_0030: ldloc.1IL_0031: ldelem.refIL_0032: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)IL_0037: nopIL_0038: nopIL_0039: ldloc.1 //IL_003a: ldc.i4.1 //IL_003b: add //索引加1,这里的索引是已经保存在堆栈中的索引IL_003c: stloc.1IL_003d: ldloc.1IL_003e: ldloc.0IL_003f: ldlenIL_0040: conv.i4IL_0041: cltIL_0043: stloc.s CS$4$0001IL_0045: ldloc.s CS$4$0001IL_0047: brtrue.s IL_002e //跳转到第2行IL_0049: nopIL_004a: ldloc.0IL_004b: stloc.s CS$6$0002IL_004d: ldc.i4.0IL_004e: stloc.s CS$7$0003IL_0050: br.s IL_0067 //foreach开始的地方IL_0052: ldloc.s CS$6$0002IL_0054: ldloc.s CS$7$0003IL_0056: ldelem.refIL_0057: stloc.2IL_0058: nopIL_0059: ldloc.2IL_005a: call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)IL_005f: nopIL_0060: nopIL_0061: ldloc.s CS$7$0003 //IL_0063: ldc.i4.1 //IL_0064: add //当前索引处加1IL_0065: stloc.s CS$7$0003IL_0067: ldloc.s CS$7$0003IL_0069: ldloc.s CS$6$0002IL_006b: ldlenIL_006c: conv.i4IL_006d: cltIL_006f: stloc.s CS$4$0001IL_0071: ldloc.s CS$4$0001IL_0073: brtrue.s IL_0052 //跳转到27行
从IL可以看出,for中循环的索引是for自身的索引(即i),foreach在循环过程中会在指定位置存储一个值,这个值就是循环用的索引。所以,其实foreach内部还是存储了一个索引值用于循环,只是我们在用的过程中没有察觉到存在这个变量而已。
我们再来看看下面这个例子:
static void RunFor(){ string[] strList = new string[]{ "1","2","3","4"}; for (int i = 0; i < strList.Length; i++){strList[i] = "1";}} static void RunForeach(){ string[] strList = new string[]{ "1","2","3","4"}; foreach (string str in strList){ str = "1";}}
编译出错 : “str”是一个“foreach 迭代变量”,无法为它赋值
static void RunFor(){string[] strList = new string[]{"1","2","3","4"};for (int i = 0; i < strList.Length; i++){strList[i] = "1";}}static void RunForeach(){string[] strList = new string[]{"1","2","3","4"};foreach (string str in strList){str = "1";}}
同样,编译器给出了相同的错误。
那么如果在foreach中移除当前项呢?
class Program{ static void Main(string[] args){List<string> strs = new List<string>() { "1", "2", "3", "4" }; foreach (string str in strs){strs.Remove(str);}Console.ReadKey();}}
运行出现了异常
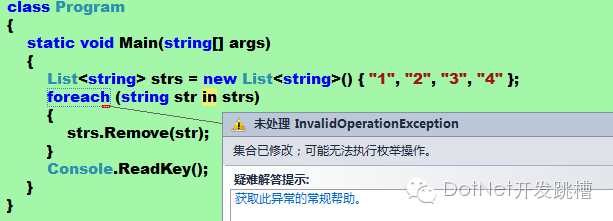
可以看出移除IEnumerable类型的变量也会出错,所以在foreach中是不能改变进行迭代的集合对象值的。
2、foreach和IEnumerable的联系
像List,Array等集合类型,可以使用for和foreach来对其进行循环迭代,获得每一个集合内的对象用于操作。之所以可以使用foreach,是因为List,Array等类型实现了IEnumerable或者IEnumerable<T>接口。
public interface IEnumerable{IEnumerator GetEnumerator();}IEnumerable接口内部只有一个方法,GetEnumerator()方法,返回值是一个IEnumerator类型的对象。
public interface IEnumerator{ bool MoveNext();object Current { get; }void Reset();}
可以看出,在IEnumerator接口中有三个成员,用于移动位置的MoveNext函数,表示当前对象的Current属性,重置函数Reset。
我们以ArrayList类型为例,来看看这个接口是怎么实现的。
首先内部有一个数组变量用于存储遍历的集合对象。
object[] _items;在内部私有的类ArrayListEnumeratorSimple中实现了IEnumerator接口成员。
public bool MoveNext(){int num;if (this.version != this.list._version){throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_EnumFailedVersion"));}if (this.isArrayList){if (this.index < (this.list._size - 1)){num = this.index + 1;this.index = num;this.currentElement = this.list._items[num]; //其实还是取得内部的数组变量的成员return true;}this.currentElement = dummyObject;this.index = this.list._size;return false;}if (this.index < (this.list.Count - 1)){num = this.index + 1;this.index = num;this.currentElement = this.list[num]; //数组变量的成员return true;}this.index = this.list.Count;this.currentElement = dummyObject;return false;}
在MoveNext中进行迭代循环的时候迭代的是内部的_items数组,即每次取的值都是_items的成员,而_items数组是ArrayList的索引数组。每次迭代后都会保存当前索引值用于下次使用。
所以不难看出,IEnumerator接口内部实现的方式归根结底还是和for实现的方式一样的。
之所以修改枚举值过后继续访问会抛出InvalidOperationException异常是因为以下代码:
if (this.version != this.list._version){throw new InvalidOperationException(Environment.GetResourceString("InvalidOperation_EnumFailedVersion"));}
在Reset和MoveNext中都有这个判断,如果枚举值被修改了,他所对应的版本号将会发生改变(在Remove函数中将会执行this._version++,使得版本号发生了改变,其他改变枚举值状态的函数类似)。
3、自定义实现迭代器
具体实现过程代码:
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){TestIEnumerable test = new TestIEnumerable();foreach (string str in test){Console.WriteLine(str);}Console.ReadKey();}}class TestIEnumerable : IEnumerable{private string[] _item;public TestIEnumerable(){_item = new string[]{"1","2","3","4"};}public string this[int index]{get { return _item[index]; }}public IEnumerator GetEnumerator(){return new EnumeratorActualize(this);}class EnumeratorActualize : IEnumerator{private int index;private TestIEnumerable _testEnumerable;private object currentObj;public EnumeratorActualize(TestIEnumerable testEnumerable){_testEnumerable = testEnumerable;currentObj = new object();index = -1;}public object Current{get{return currentObj;}}public bool MoveNext(){if (index < _testEnumerable._item.Length - 1){index++;currentObj = _testEnumerable._item[index];return true;}index = _testEnumerable._item.Length;return false;}public void Reset(){index = -1;}}}
