前言
上篇《.NET Core高性能对象转换》简单实现了对象映射,针对数组,集合,嵌套类并没有给出实现,这一篇继续完善细节。
开源对象映射类库映射分析
1.AutoMapper
实现原理:主要通过表达式树Api 实现对象映射 .
优点: .net功能最全的对象映射类库。
缺点:当出现复杂类型和嵌套类型时性能直线下降,甚至不如序列化快
2.TinyMapper
实现原理:主要通过Emit 实现对象映射
优点:速度非常快。在处理复杂类型和嵌套类型性能也很好
缺点:相对AutoMapper功能上少一些,Emit的实现方案,在代码阅读和调试上相对比较麻烦,而表达式树直接观察 DebugView中生成的代码结构便可知道问题所在
3. 本文的对象映射库
针对AutoMapper 处理复杂类型和嵌套类型时性能非常差的情况,自己实现一个表达式树版的高性能方案
此篇记录下实现对象映射库的过程
构造测试类
public class TestA
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public TestC TestClass { get; set; }
public IEnumerable<TestC> TestLists { get; set; }
}
public class TestB
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public TestD TestClass { get; set; }
public TestD[] TestLists { get; set; }
}
public class TestC
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public TestC SelfClass { get; set; }
}
public class TestD
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public TestD SelfClass { get; set; }
}
1、初步实现
利用表达式树给属性赋值 利用 Expresstion.New构造 var b=new B{};
private static Func<TSource, TTarget> GetMap<TSource, TTarget>()
{
var sourceType = typeof(TSource);
var targetType = typeof(TTarget);
//构造 p=>
var parameterExpression = Expression.Parameter(sourceType, "p");
//构造 p=>new TTarget{ Id=p.Id,Name=p.Name };
var memberBindingList = new List<MemberBinding>();
foreach (var sourceItem in sourceType.GetProperties())
{
var targetItem = targetType.GetProperty(sourceItem.Name);
if (targetItem == null || sourceItem.PropertyType != targetItem.PropertyType)
continue;
var property = Expression.Property(parameterExpression, sourceItem);
var memberBinding = Expression.Bind(targetItem, property);
memberBindingList.Add(memberBinding);
}
var memberInitExpression = Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(targetType), memberBindingList);
var lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TSource, TTarget>>(memberInitExpression, parameterExpression );
Console.WriteLine(lambda);
return lambda.Compile();
}
调用如下
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var testA = new TestA { Id = 1, Name = "张三" };
var func = Map<TestA, TestB>();
TestB testB = func(testA);
Console.WriteLine($"testB.Id={testB.Id},testB.Name={testB.Name}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
输出结果
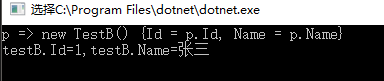
总结:此方法需要调用前需要手动编译下,然后再调用委托没有缓存委托,相对麻烦。
2、缓存实现
利用静态泛型类缓存泛型委托
public class DataMapper<TSource, TTarget>
{
private static Func<TSource, TTarget> MapFunc { get; set; }
public static TTarget Map(TSource source)
{
if (MapFunc == null)
MapFunc = GetMap();//方法在上边
return MapFunc(source);
}
}
调用方法
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var testA = new TestA { Id = 1, Name = "张三" };
TestB testB = DataMapper<TestA, TestB>.Map(testA);//委托不存在时自动生成,存在时调用静态缓存
Console.WriteLine($"testB.Id={testB.Id},testB.Name={testB.Name}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
输出结果
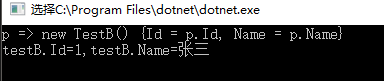
总结:引入静态泛型类能解决泛型委托缓存提高性能,但是有两个问题 1.当传入参数为null时 则会抛出空引用异常 2.出现复杂类型上述方法便不能满足了
3、解决参数为空值和复杂类型的问题
首先先用常规代码实现下带有复杂类型赋值的情况
public TestB GetTestB(TestA testA)
{
TestB testB;
if (testA != null)
{
testB = new TestB();
testB.Id = testA.Id;
testB.Name = testA.Name;
if (testA.TestClass != null)
{
testB.TestClass = new TestD();
testB.TestClass.Id = testA.TestClass.Id;
testB.TestClass.Name = testA.TestClass.Name;
}
}
else
{
testB = null;
}
return testB;
}
将上面的代码翻译成表达式树
private static Func<TSource, TTarget> GetMap()
{
var sourceType = typeof(TSource);
var targetType = typeof(TTarget);
//Func委托传入变量
var parameter = Expression.Parameter(sourceType);
//声明一个返回值变量
var variable = Expression.Variable(targetType);
//创建一个if条件表达式
var test = Expression.NotEqual(parameter, Expression.Constant(null, sourceType));// p==null;
var ifTrue = Expression.Block(GetExpression(parameter, variable, sourceType, targetType));
var IfThen = Expression.IfThen(test, ifTrue);
//构造代码块
var block = Expression.Block(new[] { variable }, parameter, IfThen, variable);
var lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<TSource, TTarget>>(block, parameter);
return lambda.Compile();
}
private static List<Expression> GetExpression(Expression parameter, Expression variable, Type sourceType, Type targetType)
{
//创建一个表达式集合
var expressions = new List<Expression>();
expressions.Add(Expression.Assign(variable, Expression.MemberInit(Expression.New(targetType))));
foreach (var targetItem in targetType.GetProperties().Where(x => x.PropertyType.IsPublic && x.CanWrite))
{
var sourceItem = sourceType.GetProperty(targetItem.Name);
//判断实体的读写权限
if (sourceItem == null || !sourceItem.CanRead || sourceItem.PropertyType.IsNotPublic)
continue;
var sourceProperty = Expression.Property(parameter, sourceItem);
var targetProperty = Expression.Property(variable, targetItem);
//判断都是class 且类型不相同时
if (targetItem.PropertyType.IsClass && sourceItem.PropertyType.IsClass && targetItem.PropertyType != sourceItem.PropertyType)
{
if (targetItem.PropertyType != targetType)//不处理嵌套循环的情况
{
//由于类型是class 所以默认值是null
var testItem = Expression.NotEqual(sourceProperty, Expression.Constant(null, sourceItem.PropertyType));
var itemExpressions = GetExpression(sourceProperty, targetProperty, sourceItem.PropertyType, targetItem.PropertyType);
var ifTrueItem = Expression.Block(itemExpressions);
var IfThenItem = Expression.IfThen(testItem, ifTrueItem);
expressions.Add(IfThenItem);
continue;
}
}
//目标值类型时 且两者类型不一致时跳过
if (targetItem.PropertyType != sourceItem.PropertyType)
continue;
expressions.Add(Expression.Assign(targetProperty, sourceProperty));
}
return expressions;
}
总结:此方案,运用 Expression.IfThen(testItem, ifTrueItem) 判断空值问题,通过递归调用 GetExpression()方法,处理复杂类型。
但是。。。针对嵌套类仍然不能解决。因为表达式树是在实际调用方法之前就生成的,在没有实际的
参数值传入之前,生成的表达式是不知道有多少层级的。
有个比较low的方案是,预先设定嵌套层级为10层,然后生成一个有10层 if(P!=null) 的判断。如果传入的参数层级超过10层了呢,就得手动调整生成的树,此方案也否决。
最后得出的结论只能在表达式中动态调用方法。
4、最终版本
通过动态调用方法解决嵌套类,代码如下
using System.Collections;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
using static System.Linq.Expressions.Expression;
public static class Mapper<TSource, TTarget> where TSource : class where TTarget : class
{
private static Func<TSource, TTarget> MapFunc { get; set; }
public static TTarget Map(TSource source)
{
if (MapFunc == null)
MapFunc = GetMap();
return MapFunc(source);
}
public static List<TTarget> MapList(IEnumerable<TSource> sources)
{
if (MapFunc == null)
MapFunc = GetMap();
var result = new List<TTarget>();
foreach (var item in sources)
{
result.Add(MapFunc(item));
}
return result;
}
private static Func<TSource, TTarget> GetMap()
{
var sourceType = typeof(TSource);
var targetType = typeof(TTarget);
//Func委托传入变量
var parameter = Parameter(sourceType, "p");
var memberBindings = new List<MemberBinding>();
var targetTypes = targetType.GetProperties().Where(x => x.PropertyType.IsPublic && x.CanWrite);
foreach (var targetItem in targetTypes)
{
var sourceItem = sourceType.GetProperty(targetItem.Name);
//判断实体的读写权限
if (sourceItem == null || !sourceItem.CanRead || sourceItem.PropertyType.IsNotPublic)
continue;
//标注NotMapped特性的属性忽略转换
if (sourceItem.GetCustomAttribute<NotMappedAttribute>() != null)
continue;
var sourceProperty = Property(parameter, sourceItem);
//当非值类型且类型不相同时
if (!sourceItem.PropertyType.IsValueType && sourceItem.PropertyType != targetItem.PropertyType)
{
//判断都是(非泛型)class
if (sourceItem.PropertyType.IsClass && targetItem.PropertyType.IsClass &&
!sourceItem.PropertyType.IsGenericType && !targetItem.PropertyType.IsGenericType)
{
var expression = GetClassExpression(sourceProperty, sourceItem.PropertyType, targetItem.PropertyType);
memberBindings.Add(Expression.Bind(targetItem, expression));
}
//集合数组类型的转换
if (typeof(IEnumerable).IsAssignableFrom(sourceItem.PropertyType) && typeof(IEnumerable).IsAssignableFrom(targetItem.PropertyType))
{
var expression = GetListExpression(sourceProperty, sourceItem.PropertyType, targetItem.PropertyType);
memberBindings.Add(Expression.Bind(targetItem, expression));
}
continue;
}
if (targetItem.PropertyType != sourceItem.PropertyType)
continue;
memberBindings.Add(Bind(targetItem, sourceProperty));
}
//创建一个if条件表达式
var test = NotEqual(parameter, Constant(null, sourceType));// p==null;
var ifTrue = MemberInit(New(targetType), memberBindings);
var condition = Condition(test, ifTrue, Constant(null, targetType));
var lambda = Lambda<Func<TSource, TTarget>>(condition, parameter);
return lambda.Compile();
}
/// <summary>
/// 类型是clas时赋值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sourceProperty"></param>
/// <param name="targetProperty"></param>
/// <param name="sourceType"></param>
/// <param name="targetType"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static Expression GetClassExpression(Expression sourceProperty, Type sourceType, Type targetType)
{
//条件p.Item!=null
var testItem = NotEqual(sourceProperty, Constant(null, sourceType));
//构造回调 Mapper<TSource, TTarget>.Map()
var mapperType = typeof(Mapper<,>).MakeGenericType(sourceType, targetType);
var iftrue = Call(mapperType.GetMethod(nameof(Map), new[] { sourceType }), sourceProperty);
var conditionItem = Condition(testItem, iftrue, Constant(null, targetType));
return conditionItem;
}
/// <summary>
/// 类型为集合时赋值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="sourceProperty"></param>
/// <param name="targetProperty"></param>
/// <param name="sourceType"></param>
/// <param name="targetType"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static Expression GetListExpression(Expression sourceProperty, Type sourceType, Type targetType)
{
//条件p.Item!=null
var testItem = NotEqual(sourceProperty, Constant(null, sourceType));
//构造回调 Mapper<TSource, TTarget>.MapList()
var sourceArg = sourceType.IsArray ? sourceType.GetElementType() : sourceType.GetGenericArguments()[0];
var targetArg = targetType.IsArray ? targetType.GetElementType() : targetType.GetGenericArguments()[0];
var mapperType = typeof(Mapper<,>).MakeGenericType(sourceArg, targetArg);
var mapperExecMap = Call(mapperType.GetMethod(nameof(MapList), new[] { sourceType }), sourceProperty);
Expression iftrue;
if (targetType == mapperExecMap.Type)
{
iftrue = mapperExecMap;
}
else if (targetType.IsArray)//数组类型调用ToArray()方法
{
iftrue = Call(mapperExecMap, mapperExecMap.Type.GetMethod("ToArray"));
}
else if (typeof(IDictionary).IsAssignableFrom(targetType))
{
iftrue = Constant(null, targetType);//字典类型不转换
}
else
{
iftrue = Convert(mapperExecMap, targetType);
}
var conditionItem = Condition(testItem, iftrue, Constant(null, targetType));
return conditionItem;
}
}
输出的 表达式

格式化后
p => IIF((p != null),
new TestB()
{
Id = p.Id,
Name = p.Name,
TestClass = IIF(
(p.TestClass != null),
Map(p.TestClass),
null
),
TestLists = IIF(
(p.TestLists != null),
MapList(p.TestLists).ToArray(),
null
)
},
null)
说明 Map(p.TestClass) MapList(p.TestLists).ToArray(), 完整的信息为 Mapper<TestC,TestD>.Map() Mapper<TestC,TestD>.MapList()
总结:解决嵌套类的核心代码
//构造回调 Mapper<TSource, TTarget>.Map()
var mapperType = typeof(DataMapper<,>).MakeGenericType(sourceType, targetType);
var mapperExecMap = Expression.Call(mapperType.GetMethod(nameof(Map), new[] { sourceType }), sourceProperty);
利用Expression.Call 根据参数类型动态生成 对象映射的表达式
性能测试
写了这么多最终目的还是为了解决性能问题,下面将对比下性能
1、测试类
public static class MapperTest
{
//执行次数
public static int Count = 100000;
//简单类型
public static void Nomal()
{
Console.WriteLine($"******************简单类型:{Count / 10000}万次执行时间*****************");
var model = new TestA
{
Id =1,
Name = "张三",
};
//计时
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
if (model != null)
{
var b = new TestB
{
Id = model.Id,
Name = model.Name,
};
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"原生的时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Exec(model);
}
//复杂类型
public static void Complex()
{
Console.WriteLine($"********************复杂类型:{Count / 10000}万次执行时间*********************");
var model = new TestA
{
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
TestClass = new TestC
{
Id = 2,
Name = "lisi",
},
};
//计时
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
if (model != null)
{
var b = new TestB
{
Id = model.Id,
Name = model.Name,
};
if (model.TestClass != null)
{
b.TestClass = new TestD
{
Id = i,
Name = "lisi",
};
}
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"原生的时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Exec(model);
}
//嵌套类型
public static void Nest()
{
Console.WriteLine($"*****************嵌套类型:{Count / 10000}万次执行时间*************************");
var model = new TestA
{
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
TestClass = new TestC
{
Id = 1,
Name = "lisi",
SelfClass = new TestC
{
Id = 2,
Name = "lisi",
SelfClass = new TestC
{
Id = 3,
Name = "lisi",
SelfClass = new TestC
{
Id = 4,
Name = "lisi",
},
},
},
},
};
//计时
var item = model;
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
//这里每一步需要做非空判断的,书写太麻烦省去了
if (model != null)
{
var b = new TestB
{
Id = model.Id,
Name = model.Name,
TestClass = new TestD
{
Id = model.TestClass.Id,
Name = model.TestClass.Name,
SelfClass = new TestD
{
Id = model.TestClass.SelfClass.Id,
Name = model.TestClass.SelfClass.Name,
SelfClass = new TestD
{
Id = model.TestClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.Id,
Name = model.TestClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.Name,
SelfClass = new TestD
{
Id = model.TestClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.Id,
Name = model.TestClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.SelfClass.Name,
},
},
},
},
};
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"原生的时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Exec(model);
}
//集合
public static void List()
{
Console.WriteLine($"********************集合类型:{Count/10000}万次执行时间***************************");
var model = new TestA
{
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
TestLists = new List<TestC> {
new TestC{
Id = 1,
Name = "张三",
},
new TestC{
Id = -1,
Name = "张三",
},
}
};
//计时
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
var item = model;
if (item != null)
{
var b = new TestB
{
Id = item.Id,
Name = item.Name,
TestLists = new List<TestD> {
new TestD{
Id = item.Id,
Name = item.Name,
},
new TestD{
Id = -item.Id,
Name = item.Name,
},
}.ToArray()
};
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"原生的时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
Exec(model);
}
public static void Exec(TestA model)
{
//表达式
Mapper<TestA, TestB>.Map(model);
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
var b = Mapper<TestA, TestB>.Map(model);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"表达式的时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
//AutoMapper
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
var b = AutoMapper.Mapper.Map<TestA, TestB>(model);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"AutoMapper时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
//TinyMapper
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < Count; i++)
{
var b = TinyMapper.Map<TestA, TestB>(model);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"TinyMapper时间:{sw.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
}
}
2、调用测试
static void Main(string[] args)
{
AutoMapper.Mapper.Initialize(cfg => cfg.CreateMap<TestA, TestB>());
TinyMapper.Bind<TestA, TestB>();
Mapper<TestA, TestB>.Map(new TestA());
MapperTest.Count = 10000;
MapperTest.Nomal();
MapperTest.Complex();
MapperTest.Nest();
MapperTest.List();
MapperTest.Count = 100000;
MapperTest.Nomal();
MapperTest.Complex();
MapperTest.Nest();
MapperTest.List();
MapperTest.Count = 1000000;
MapperTest.Nomal();
MapperTest.Complex();
MapperTest.Nest();
MapperTest.List();
MapperTest.Count = 10000000;
MapperTest.Nomal();
MapperTest.Complex();
MapperTest.Nest();
MapperTest.List();
Console.WriteLine($"------------结束--------------------");
Console.ReadLine();
}
3、结果
1万次
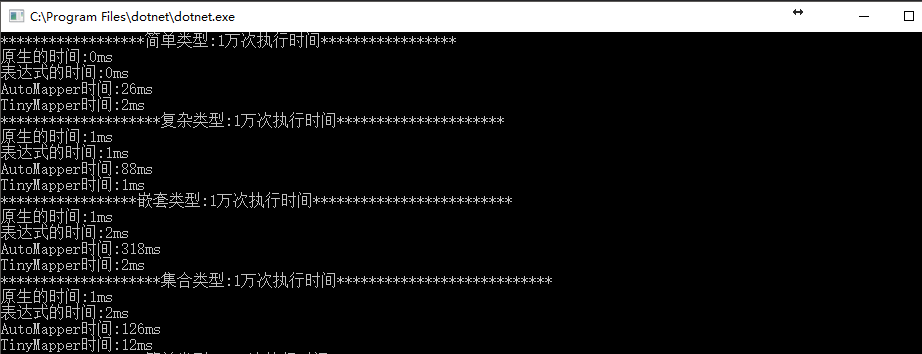
10万次
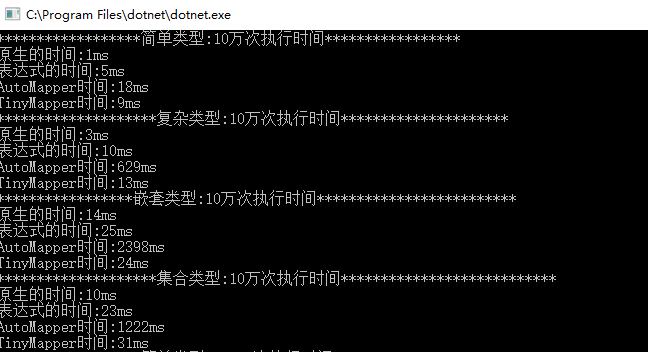
100万次
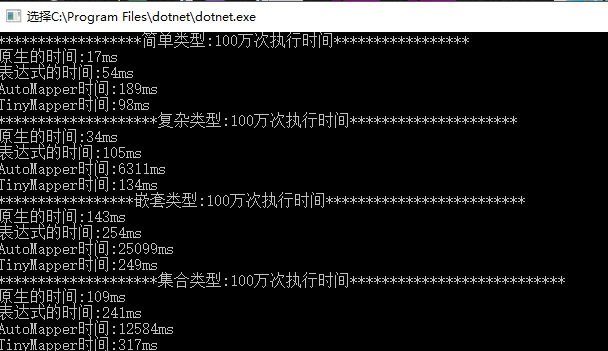
1000万次
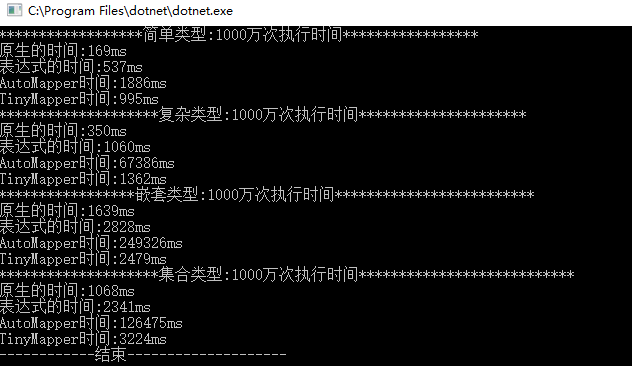
上图结果AutoMapper 在非简单类型的转换上比其他方案有50倍以上的差距,几乎就跟反射的结果一样。
