前言
对于 Thread 和 ThreadPool 已经是元老级别的类了。Thread 是 C# 语言对线程对象的封装,它从 .NET 1.0 版本就有了,然后 ThreadPool 是 .Net Framework 2.0 版本中出现的,都是相当成熟的存在。
当然,现在已经出现了 Task 和 PLinq 等更高效率的并发类,线程和线程池在实际开发中逐渐减少了,但是不能不知道他们的用法,因为总有需要对接的内容,别人用了你也得能看懂。.
本文将结合示例,简单介绍下 Thread 和 ThreadPool。
一、Thread 类
Thread 类的功能就是,创建和控制线程,设置其优先级并获取其状态。
下边代码简单示例说明下 Thread 的相关内容:
public static void Main()
{
// (1)
//var th1 = new Thread(ExecuteInForeground);
//th1.Start();
// (2)
//var th2 = new Thread(ExecuteInForeground);
//th2.IsBackground = true;
//th2.Start();
// (3)
//ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ExecuteInForeground);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
// Console.WriteLine($"主线程 ({Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}) 即将退出 执行 Join() 方法。。。");
// th2.Join();
Console.WriteLine($"主线程 ({Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId}) 即将退出。。。");
//Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void ExecuteInForeground(object state)
{
var sw = Stopwatch.StartNew();
Console.WriteLine("线程 {0}: {1}, 优先级: {2}",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,
Thread.CurrentThread.ThreadState,
Thread.CurrentThread.Priority);
do
{
Console.WriteLine("线程 {0}: 计时 {1:N2} 秒",
Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId,
sw.ElapsedMilliseconds / 1000.0);
Thread.Sleep(500);
} while (sw.ElapsedMilliseconds <= 5000);
sw.Stop();
}
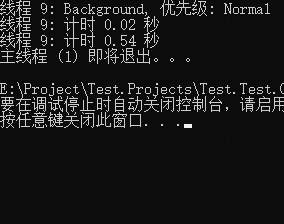
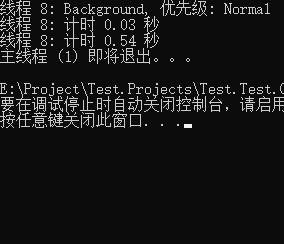
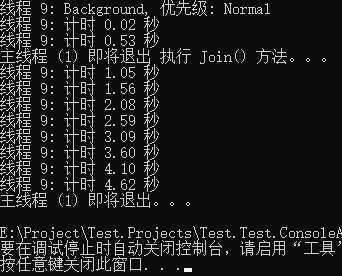
注释部分三组线程启动的结果如下三图
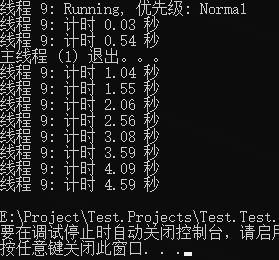
第 1 部分,是前台线程,必须运行完毕,主线程才会退出,所以一直运行到 5s 之前。
第 2、3 部分,均为后台线程,当主线程运行完成之时,无论是否运行完成直接中断,所以只循环了两次就退出了。
关于 Join() 方法
代码中th2.Join()如果在后台线程上执行,这结果如下图,将会等待后台线程完成后主线程才结束。
二、ThreadPool 类
由于线程对象的创建时需要分配内存,GC 过程中销毁对象,然后整合零散的内存块,从而占用 CPU 资源,会影响程序性能,所以 ThreadPool 诞生了。
使用线程池,可以通过向应用程序提供由系统管理的工作线程池,来更有效的使用线程。
线程池可以通过重用线程、控制线程数量等操作,减少频繁创建和切换线程所带来的开销,从而提高响应速度。
可直接使用线程池中空闲的线程,而不必等待线程的创建,方便管理线程。
注意,托管线程池中的线程是后台线程,其 IsBackground 属性为 true。
1、ThreadPool 的几个属性值
CompletedWorkItemCount:获取迄今为止已处理的工作项数。
PendingWorkItemCount:获取当前已加入处理队列的工作项数。
ThreadCount:获取当前存在的线程池线程数。
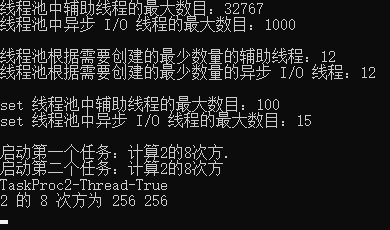
下面是一个关于线程池的几个属性值,以及开启新的后台线程并传入参数的实例:
//存放要计算的数值的字段
public static double num1 = -1;
public static double num2 = -1;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int workerThreads, completionPortThreads;
// public static void GetMaxThreads (out int workerThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out workerThreads, out completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"线程池中辅助线程的最大数目:{workerThreads}");
Console.WriteLine($"线程池中异步 I/O 线程的最大数目:{completionPortThreads}");
Console.WriteLine();
// public static void GetMinThreads(out int workerThreads, out int completionPortThreads);
ThreadPool.GetMinThreads(out workerThreads, out completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"线程池根据需要创建的最少数量的辅助线程:{workerThreads}");
Console.WriteLine($"线程池根据需要创建的最少数量的异步 I/O 线程:{completionPortThreads}");
Console.WriteLine();
ThreadPool.SetMaxThreads(100, 15); // set 的值必须是 Min~Max 之间的值,否则会设置不成功
ThreadPool.GetMaxThreads(out workerThreads, out completionPortThreads);
Console.WriteLine($"set 线程池中辅助线程的最大数目:{workerThreads}");
Console.WriteLine($"set 线程池中异步 I/O 线程的最大数目:{completionPortThreads}");
Console.WriteLine();
// 命名参数 传入后台线程
int num = 2;
// 启动第一个任务:计算x的8次方
Console.WriteLine("启动第一个任务:计算{0}的8次方.", num);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(TaskProc1), num);
// 启动第二个任务
Console.WriteLine("启动第二个任务:计算{0}的8次方", num);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(new WaitCallback(TaskProc2), num);
// 等待两个数值等完成计算
while (num1 == -1 || num2 == -1) ;
//打印计算结果
Console.WriteLine($"{num} 的 8 次方为 {num1} {num2}");
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void TaskProc2(object state)
{
Console.WriteLine($"TaskProc2-Thread-{Thread.CurrentThread.IsBackground}");
num1 = Math.Pow(Convert.ToDouble(state), 8);
}
private static void TaskProc1(object state)
{
num2 = Math.Pow(Convert.ToDouble(state), 8);
}
输出结果
2、由线程池生成一个可以取消的后台线程
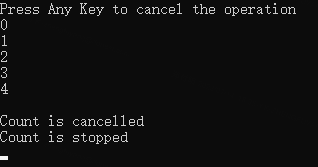
如下代码,在没有单击回车键之前,程序会一直打印递增数字,当收到回车指令后,cts.Cancel();被执行,后台线程就取消成功了。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t => Counts(cts.Token, 1000));
Console.WriteLine("Press Any Key to cancel the operation");
Console.ReadLine();
cts.Cancel();
Console.ReadLine();
}
private static void Counts(CancellationToken token, int CountTo)
{
for (int count = 0; count < CountTo; count++)
{
if (token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
Console.WriteLine("Count is cancelled");
break;
}
Console.WriteLine(count);
Thread.Sleep(200);
}
Console.WriteLine("Count is stopped");
}
结果如下图
三、Thread 和 ThreadPool 性能比较
如下代码,分别执行 100 次,看最终需要的时间成本
public static void Main()
{
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Thread th = new Thread(() =>
{
int count = 0;
count++;
});
th.Start();
}
sw.Stop();
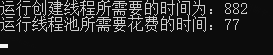
Console.WriteLine("运行创建线程所需要的时间为:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(t =>
{
int count = 0;
count++;
});
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("运行线程池所需要花费的时间:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.ReadLine();
}
如下图,明显线程池性能更佳