计数器、WMI
获取设备的内存信息,如系统可用运行内存:.
public static async Task<double> GetMemoryAvailableAsync(FileSizeUnit fileSizeUnit = FileSizeUnit.GB){return await Task.Run(() =>{using var managementClass = new ManagementClass("Win32_PerfFormattedData_PerfOS_Memory");using var instances = managementClass.GetInstances();double available = 0;foreach (var mo in instances){//AvailableMBytes单位是MBvar size = long.Parse(mo.Properties["AvailableMBytes"].Value.ToString()) * 1024 * 1024;available += size.ConvertTo(fileSizeUnit);}return available;});}
以上是ManagementClass方式实现,还有ManagementObjectSearcher,都是WMI检索查询。
WMI查询比较慢,上面一段耗时在200ms+。
还有一种用得较多的,PerformanceCounter性能计数器,以CPU获取为例:
public static async Task<double> GetUsageByCounterAsync(){//CPU计数器using var pcCpuUsage = new PerformanceCounter("Processor", "% Processor Time", "_Total") { MachineName = "." };// NextValue首次会返回0,所以需要加个延时下次再获取值pcCpuUsage.NextValue();await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(500));var cpuUsed = pcCpuUsage.NextValue();return cpuUsed;}
性能计数器,也有一定的耗时40ms以上。另外因为得它实现方式,初始化后无法第一次获取到真正数值,需要间隔一段时间再去拿。所以此方案实际耗时挺高
WMI、性能计数器,昨天遇到了使用异常:

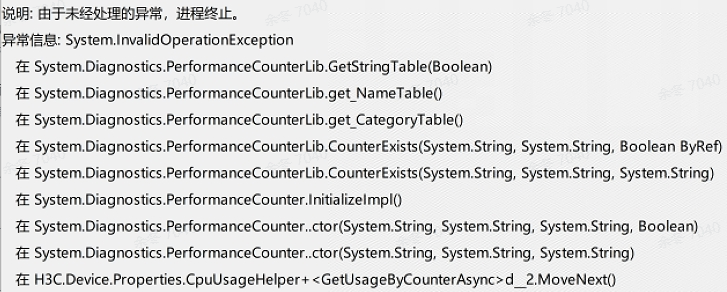
看源码,计数器是注册表PerformanceData位置损坏了,而Management是IWbemServices获取状态码ErrorCode异常。
PerformanceCounter是WMI,而WMI是基于WBEM协议实现的,所以我理解成上面的异常其实是一类问题。
官网有对此类异常有一些描述:重新生成性能计数器库值 - Windows Server | Microsoft Learn

所以基于PerformanceCounter、ManagementClass以及ManagementObjectSearcher的实现,有一定风险。
kernel32
kernel32下有个函数可以获取内存状态
[DllImport("kernel32.dll")][return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]static extern bool GlobalMemoryStatusEx(ref MEMORYINFO mi);
以下是获取可用运行内存的实现:
//Define the information structure of memory[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]struct MEMORYINFO{public uint dwLength; //Current structure sizepublic uint dwMemoryLoad; //Current memory utilizationpublic ulong ullTotalPhys; //Total physical memory sizepublic ulong ullAvailPhys; //Available physical memory sizepublic ulong ullTotalPageFile; //Total Exchange File Sizepublic ulong ullAvailPageFile; //Total Exchange File Sizepublic ulong ullTotalVirtual; //Total virtual memory sizepublic ulong ullAvailVirtual; //Available virtual memory sizepublic ulong ullAvailExtendedVirtual; //Keep this value always zero}/// <summary>/// Get the current memory usage/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>private static MEMORYINFO GetMemoryStatus(){MEMORYINFO memoryInfo = new MEMORYINFO();memoryInfo.dwLength = (uint)System.Runtime.InteropServices.Marshal.SizeOf(memoryInfo);GlobalMemoryStatusEx(ref memoryInfo);return memoryInfo;}/// <summary>/// 获取系统可用运行内存/// </summary>/// <param name="fileSizeUnit">默认单位GB</param>/// <returns></returns>public static double GetMemoryAvailable(FileSizeUnit fileSizeUnit = FileSizeUnit.GB){var memoryStatus = GetMemoryStatus();var memoryAvailable = ((long)memoryStatus.ullAvailPhys).ConvertTo(fileSizeUnit);return memoryAvailable;}
上述方式,获取速度超快,几乎不耗时。
通过Kernel32-GetSystemTimes方式,获取CPU信息(CPU比例计算逻辑,代码略多点):
/// <summary>/// 获取CPU占用率/使用率(单位:%)/// </summary>/// <returns></returns>public static async Task<double> GetUsageByKernelAsync(){long idleTime1 = 0;long kernelTime1 = 0;long userTime1 = 0;if (GetSystemTimes(out var lpIdleTime, out var lpKernelTime, out var lpUserTime)){idleTime1 = lpIdleTime;kernelTime1 = lpKernelTime;userTime1 = lpUserTime;}//添加俩次获取CPU信息的间隔await Task.Delay(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5));long idleTime2 = 0;long kernelTime2 = 0;long userTime2 = 0;if (GetSystemTimes(out var lpIdleTime2, out var lpKernelTime2, out var lpUserTime2)){idleTime2 = lpIdleTime2;kernelTime2 = lpKernelTime2;userTime2 = lpUserTime2;}//分别获取到用户时间、内核时间、空闲时间var userTime = userTime2 - userTime1;var kernelTime = kernelTime2 - kernelTime1;var idleTime = idleTime2 - idleTime1;//计算Cpu占用率。计算公式:用户时间+内核时间-空闲时间/用户时间+内核时间var systemTotal = kernelTime + userTime;var cpu = (systemTotal - idleTime) * 10000 / systemTotal;return cpu / 100.0;}/// <summary>/// 获取系统CPU时间数据/// </summary>/// <param name="lpIdleTime">空闲时间</param>/// <param name="lpKernelTime">内核时间</param>/// <param name="lpUserTime">用户时间</param>/// <returns></returns>[DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)]static extern bool GetSystemTimes(out long lpIdleTime, out long lpKernelTime, out long lpUserTime);
另外,也有一种途径可以获取到内存信息,引用程序集Microsoft.VisualBasic,Microsoft.VisualBasic.Devices下有个ComputerInfo类
var physicalMemory = new Microsoft.VisualBasic.Devices.ComputerInfo().AvailablePhysicalMemory;
可以拿到可用内存、总内存,不过CPU信息是没有的。
ComputerInfo的内部源码,我标注了下:
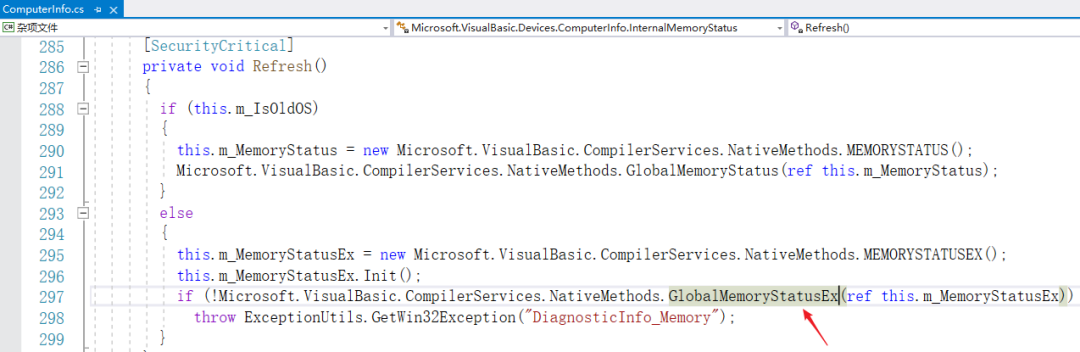
所以ComputerInfo,也是基于GlobalMemoryStatusEx函数做了封装,大家可以直接用。
