EF Core默认约定规则基于领域类和DbContext类创建数据库Schema,例如-表名称,列名称,表关系,主键&外键 这些都是基于契约创建的
让我们通过一个例子来了解一下约定,我们有一个项目包含了下面2个领域类,Employee和Department.
public class Employee{public int Id { get; set; }public int DepartmentId { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public string Designation { get; set; }public Department Department { get; set; }}public class Department{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<Employee> Employee { get; set; }}
public class CompanyContext : DbContext{public CompanyContext(DbContextOptions<CompanyContext> options) : base(options){}public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }}
运行EF Core migrations 数据库将创建2张表-Employee 和Department,约定负责创建数据库Schema,即表、列、关系等,让我们逐一查看它们
1.1 Table
EF Core 约定创建数据库表,表名称和DbContext中定义的DbSet<T>属性名称是相同的
public DbSet<Employee> Employee { get; set; }这是非常简单的,但是第二张表也会被创建,但是我们没有定义DbSet,这是因为EF Core会查找Employee 类发现内部引用了Department类,所以会创建Department表
在Employee类内部引用了Department类,通过该属性,EntityFrameworkCore找到Department模型实体,并在数据库中为其创建一个表
public Department Department { get; set; }1.2 Column
EF Core会根据领域类定义的属性类创建数据库表中对应的列
类似的Department表中也创建了2列(Id,Name)
引用和集合属性能够在两张表中创建关联,我们稍后将看这块内容
1.3 C# 数据类型VS SQL Server列类型
接下来我们考虑EF Core 中的数据类型是如何对应到数据库表中的数据类型,如下展示了C#数据类型和SQL Server数据库数据类型的映射关系:
| C# 数据类型 | SQL Server 数据类型 |
|---|---|
| int | int |
| string | nvarchar(Max) |
| decimal | decimal(18,2) |
| float | real |
| bool | bit |
| long | bigint() |
| datetime | datetime |
| short | smallint |
在我们这个例子中,基于这两张表的映射规则如下:
// Department tableId INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULLName VARCHAR (50) NOT NULL// Employee tableId INT IDENTITY (1, 1) NOT NULLDepartmentId INT NOT NULLName VARCHAR (100) NOT NULLDesignation VARCHAR (25) NOT NULL
1.4 Nullable Column(可空列)
可空列是针对所有的引用数据类型,例如:string,Nullable,float?
1.5 NotNull Column(非空列)
EF Core会为表的主键创建不可为空的列,像float,int,Datetime
1.6 Primary Key(主键)
2 表之间关系
SQL Server 数据库表关系有3种类型:
一对多关系
一对一关系
多对多关系
2.1 一对多关系
public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}
在两张表中创建一个多对一的关系,我们有如下4种方式:
在City类创建引用导航属性指向Country类:
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}
执行EF Core Migrations 将会在数据库City和Country表之间产生一个一对多的关系,City表包含了可为空的CountryId外键
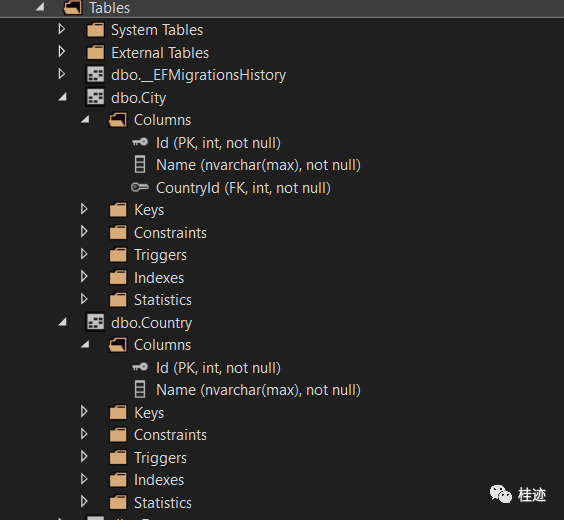
通过添加一个集合导航属性也可以创建一个一对多的关系
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property}
这种方式和契约1做相同的工作
也可以在实体中创建两个导航属性,实现一对多的关系
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property}
在这种情况下我们使用契约3的方式并且同时添加外键CountryId 属性在City实体中
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public int CountryId { get; set; } //Foreign Key entitypublic Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<City> Cities { get; set; } // Collection Navigation Property}
2.2 一对一关系
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public Country Country { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public City City { get; set; } //Reference Navigation Property}
2.3 多对多关系
在两个实体类中创建多对多关系,分别在两个实体类中创建两个集合导航属性
public class City{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<Country> Country { get; set; } //Collection Navigation Property}public class Country{public int Id { get; set; }public string Name { get; set; }public ICollection<City> City { get; set; } //Collection Navigation Property}
这个通过在数据库中添加一张名为CityCountry的表来实现,这张表将包含City和Country表的外键,我们在会讲到如何在EF Core中使用Fluent API中会讲到
总结
